bearing
A bearing is an engineering component that is used to transmit forces between moving and fixed parts of a mechanical machine, while it is made to minimize the friction that occurs between the moving and fixed parts of the machine. The bearing in the machine captures some forces, while others allow free movement.
Bearings are divided according to several criteria:
according to the prevailing direction of transmitted forces
according to construction
according to the force transmission mechanism
Division according to the captured force
Axial (most of the captured forces act in the direction of the axis of rotation)
Axial sliding
Radial (most of the captured forces act perpendicular to the axis of rotation)
Division by construction
Sliding - consist of a housing and a shaft passing through it. The bushing is usually made of self-lubricating bronze or brass, or composites or plastic (e.g. PTFE). Plain bearings are usually used where they are constantly lubricated, e.g. in combustion engines, which enables higher durability than rolling bearings. They also enable the transmission of greater forces
Rolling - contain rolling bodies of various shapes (ball, barrel, cone, roller, needle,...). They are mainly used where low resistance is required and continuous lubrication is not possible. They do not allow high speeds and large transmitted forces.
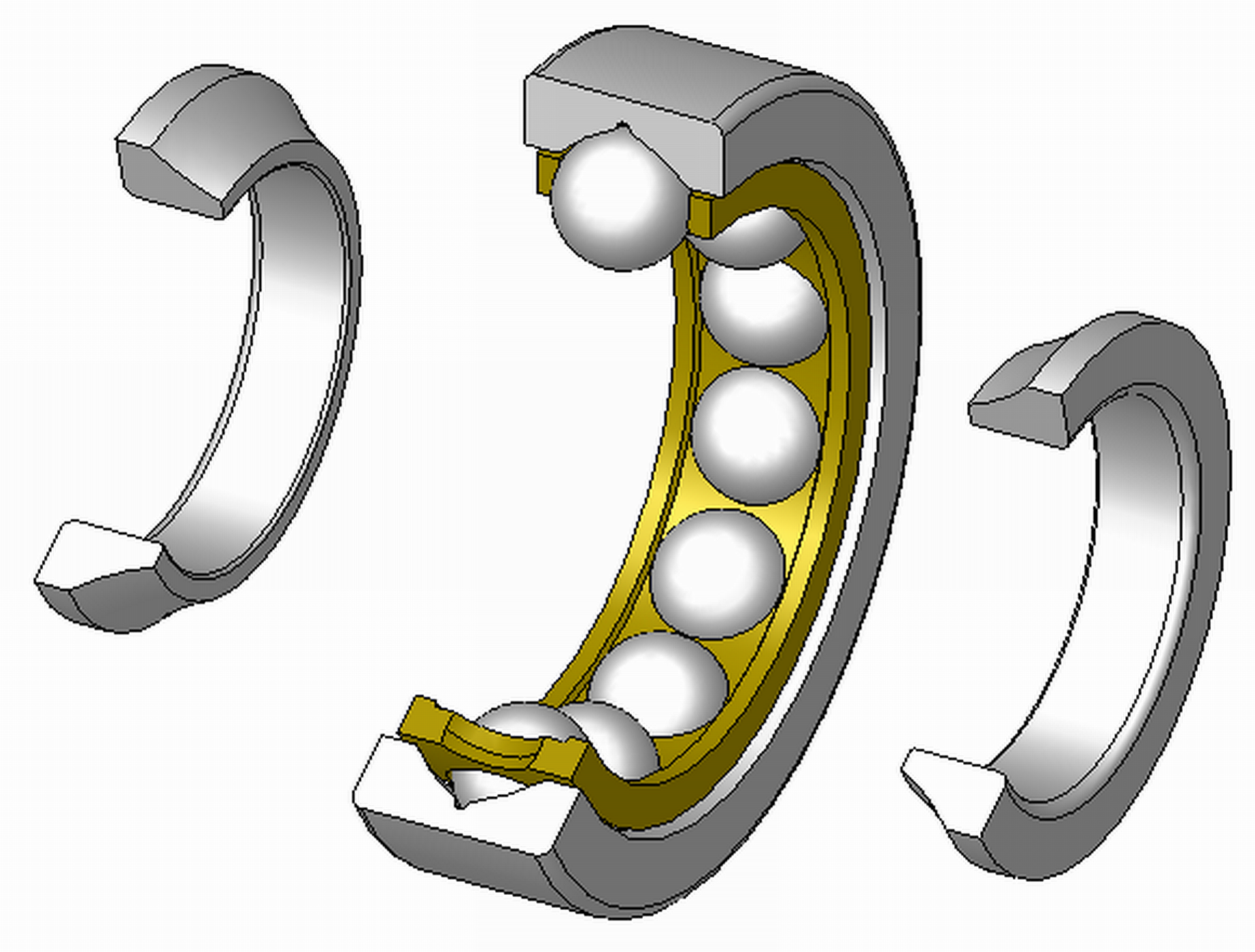
Division according to the force transmission mechanism
Slippery
Pneumatic (the driving part is on an air cushion)
Hydraulic (the driving part is on a liquid cushion)
Hydrostatic
Hydrodynamic
Rolling
Bullets
Rollers
Needles
Barrels
Conical
Magnetic
Active
Passively
